Intended for U.S. healthcare professionals only.
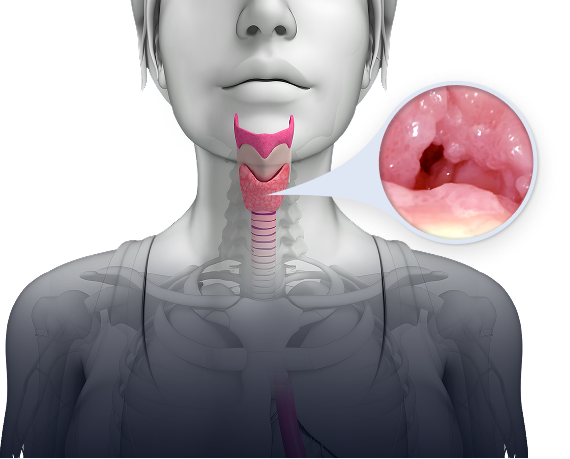
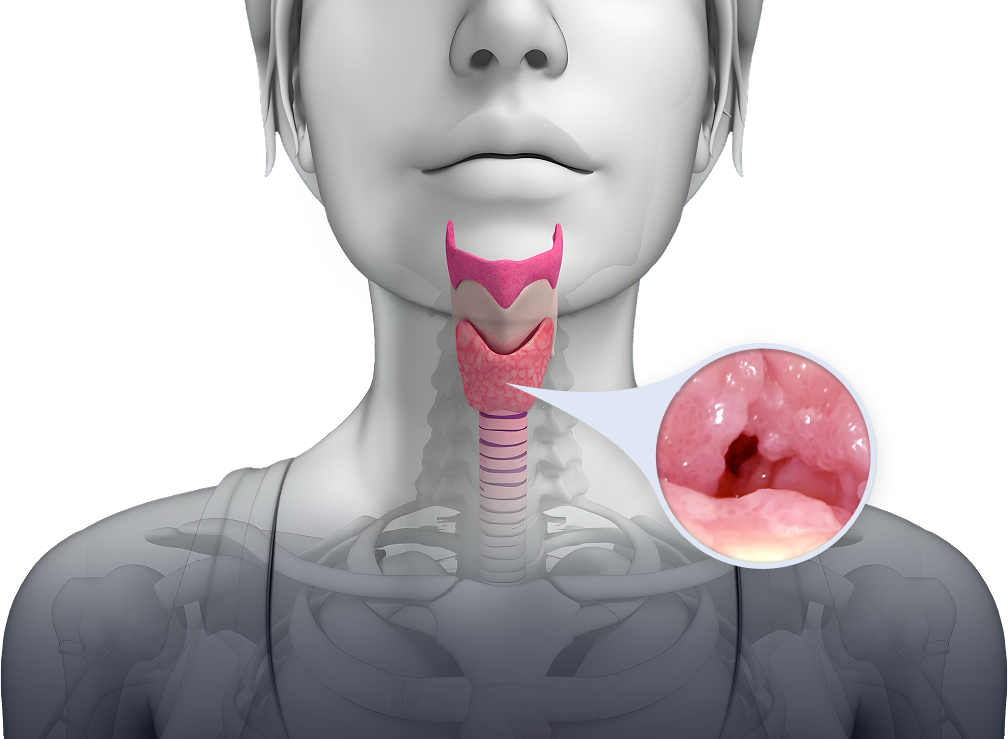
Rethink RRP
A lifetime of surgical intervention does not address the underlying cause of RRP1,2
The primary driver of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) is chronic viral infection, so ongoing surgeries do not address the underlying cause. Learn more about RRP, its diagnosis, and the management of the disease.3
RRP can have a debilitating impact on patients3,4
Chronic human papillomavirus (HPV) 6 or HPV11 infection is the primary driver of RRP, which is characterized by the growth of papillomas in the upper and lower respiratory tract that can lead to severe voice disturbance, compromised airway, and recurrent post-obstructive pneumonias. RRP can impact patients’ work and social lives, financial stability, and mental health.3,4
RRP is difficult to treat and potentially life-threatening. Although rare, RRP has the potential for transformation to malignant cancer and can be fatal. The current standard of care is repeated surgeries, which do not address the underlying cause of disease and can be associated with significant morbidity as well as significant patient burden.3,5
The most common symptoms are3:
-
DYSPNEA
-
DYSPHONIA
-
CHRONIC COUGH
Surgery alone doesn’t prevent papillomas from recurring3
Due to reactivation of latent HPV virus in remaining or adjacent tissues, papillomas can recur and require multiple surgeries.4
Current management for RRP consists of repeated laser ablation and surgical excision of papillomas to alleviate symptoms. As the number of lifetime surgeries increases, the risk for irreversible iatrogenic laryngeal injury increases with each surgery, and patients may undergo hundreds of these surgeries over their lifetimes.2,3
Patients with RRP can experience substantial impacts to daily living with decreased quality of life and high health care utilization.4

Not an actual patient.
Patients endure a lifetime of ongoing burdens from debilitating RRP2-4
13.5
LIFETIME SURGERIES
Adult patients with RRP undergo a mean of 13.5 surgical procedures2
97%
SURGICAL INJURIES
97% of patients with RRP who undergo > 10 lifetime surgeries can experience irreversible iatrogenic laryngeal injury3*
97.3%
HIGH BURDEN OF DISEASE
97.3% of patients with RRP feel debilitated by their diagnosis4
*In a single-site clinical study of patients with RRP.3
Recurrent surgeries to manage RRP can cause significant recurring risk and patient burden2,3
RRP is hard to appropriately manage—and papillomas may come back after surgery. With each surgery, patients risk surgical injuries that could lead to permanent dysphonia, face difficulties with anesthesia recovery, and experience work absences. Learn more about RRP, its diagnosis, and the management of the disease.2-4,6

Not an actual patient.
RRP can have a debilitating impact on patients3,4
Register to learn more about RRP and to get updates about this rare disease driven by a chronic viral infection.3
SIGN UPReferences: 1. Derkay CS, Bluher AE. Update on recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2019;52(4):669-679. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2019.03.011 2. Ovcinnikova O, Engelbrecht K, Verma M, Pandey R, Morais E. A systematic literature review of the epidemiology, clinical, economic and humanistic burden in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Respir Res. 2024;25(1):430. doi:10.1186/s12931-024-03057-w 3. So RJ, Hillel AT, Motz KM, Akst LM, Best SR. Factors associated with iatrogenic laryngeal injury in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024;170(4):1091-1098. doi:10.1002/ohn.629 4. So RJ, McClellan K, Best SR. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: quality of life data from an international patient registry. Laryngoscope. 2023;133(8):1919-1926. doi:10.1002/lary.30401 5. Xiao Y, Zhang X, Ma L, Wang J. Long-term outcomes of juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2021;46(1):161-167. doi:10.1111/coa.13635 6. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis patient-led FDA listening session. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Foundation. Published October 27, 2022. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://rrpf.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/RRPF-FDA-Listening-Session-Summary_FINAL_1.24.23-1.pdf